Signal Integrity Simplified Eric Bogatin
- Posted in:Admin
- 12/06/18
- 38
Teledyne LeCroy Signal Integrity Academy specializes in. Power Integrity- Simplified. Skills from the Signal Integrity Evangelist, Dr. Eric Bogatin. Signal Integrity - Simplified [Eric Bogatin] on Amazon. Rebel Bomberman Game Full Version. com. *FREE* shipping on qualifying offers. This book describes in the simplest possible terms, the signal. Signal and Power Integrity - Simplified, 3rd Edition. Bogatin ©2018. Eric currently is a Signal Integrity Evangelist with Teledyne LeCroy.
The Time Domain. Sine Waves in the Frequency Domain. Shorter Time to a Solution in the Frequency Domain. Sine Wave Features. The Fourier Transform.
The Spectrum of a Repetitive Signal. The Spectrum of an Ideal Square Wave. From the Frequency Domain to the Time Domain. Effect of Bandwidth on Rise Time. Bandwidth and Rise Time.
What Does “Significant” Mean? Bandwidth of Real Signals. Bandwidth and Clock Frequency. Bandwidth of a Measurement. Bandwidth of a Model. Bandwidth of an Interconnect. Impedance and Electrical Models.
What Is Inductance? Inductance Principle #1: There Are Circular Magnetic-Field Line Loops around All Currents. Software Cybermation 700a Manual Lymphatic Drainage. Inductance Principle #2: Inductance Is the Number of Webers of Field Line Loops around a Conductor per Amp of Current through It. Self-Inductance and Mutual Inductance. Inductance Principle #3: When the Number of Field Line Loops around a Conductor Changes, There Will Be a Voltage Induced across the Ends of the Conductor. Partial Inductance.
Effective, Total, or Net Inductance and Ground Bounce. Loop Self- and Mutual Inductance. The Power-Distribution System (PDS) and Loop Inductance. Loop Inductance per Square of Planes. Loop Inductance of Planes and Via Contacts. Loop Inductance of Planes with a Field of Clearance Holes. Loop Mutual Inductance.
Equivalent Inductance. Summary of Inductance. Current Distributions and Skin Depth. High-Permeability Materials. Eddy Currents.
The Bottom Line. The Physical Basis of Transmission Lines. Forget the Word Ground. Uniform Transmission Lines. The Speed of Electrons in Copper.
The Speed of a Signal in a Transmission Line. Spatial Extent of the Leading Edge. “Be the Signal”. The Instantaneous Impedance of a Transmission Line. Haracteristic Impedance and Controlled Impedance.
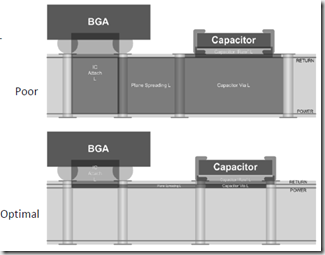
Famous Characteristic Impedances. The Impedance of a Transmission Line. Driving a Transmission Line. Return Paths. When Return Paths Switch Reference Planes.
A First-Order Model of a Transmission Line. Calculating Characteristic Impedance with Approximations. Calculating the Characteristic Impedance with a 2D Field Solver.
An n-Section Lumped Circuit Model. Frequency Variation of the Characteristic Impedance. The Bottom Line. Transmission Lines and Reflections.
Reflections at Impedance Changes. Why Are There Reflections? Reflections from Resistive Loads. Source Impedance.
Bounce Diagrams. Simulating Reflected Waveforms. Measuring Reflections with a TDR.
Transmission Lines and Unintentional Discontinuities. When to Terminate. The Most Common Termination Strategy for Point-to-Point Topology. Reflections from Short Series Transmission Lines. Reflections from Short-Stub Transmission Lines.
Reflections from Capacitive End Terminations. Reflections from Capacitive Loads in the Middle of a Trace. Capacitive Delay Adders. Effects of Corners and Vias. Loaded Lines.
Reflections from Inductive Discontinuities. The Bottom Line. Lossy Lines, Rise-Time Degradation, and Material Properties. Why Worry About Lossy Lines. Huawei Android Unlocker V1 on this page. Losses in Transmission Lines. Sources of Loss: Conductor Resistance and Skin Depth. Sources of Loss: The Dielectric.